This post contains affiliate links. This means I will make a commission at no extra cost to you should you click through and make a purchase [ “As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.” ]. Read the full disclosure here.
2006 Acura TL Alternator GuideMechanic.Com When it comes to the 2006 Acura TL, the alternator plays a crucial role in keeping the vehicle’s electrical system running smoothly.
As an essential component of the car’s charging system, the alternator ensures that the battery remains charged while powering various electrical components.
In this comprehensive blog article, we will delve into the intricacies of the 2006 Acura TL alternator, discussing its functions, common issues, and maintenance tips.
Understanding the Basics of the Acura TL Alternator
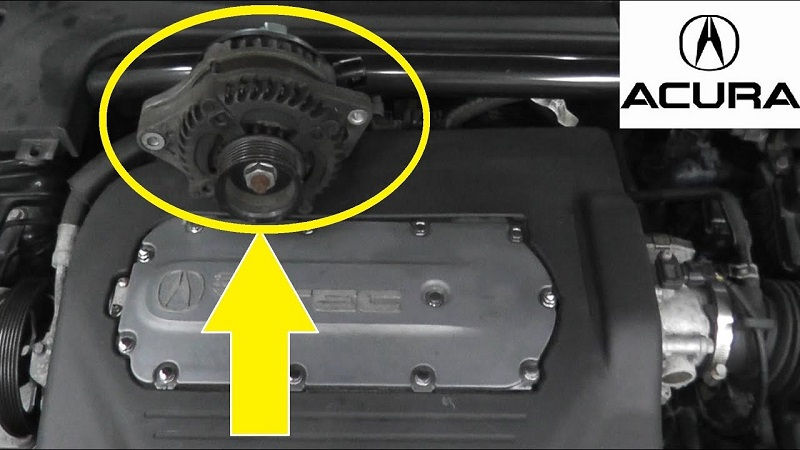
The alternator in the 2006 Acura TL is a compact, belt-driven device responsible for converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
It is connected to the engine’s crankshaft via a serpentine belt, which drives the alternator pulley. When the engine is running, the crankshaft rotation drives the alternator, causing it to generate alternating current (AC).
This AC current is then converted into direct current (DC) by a rectifier inside the alternator. The DC current is used to charge the battery and power the electrical components of the vehicle.
The alternator also houses a voltage regulator, which ensures that the electrical system operates within a specific voltage range.
It regulates the output voltage of the alternator, preventing it from exceeding safe levels and protecting sensitive electronic components from damage.
Components of the Acura TL Alternator:
The Acura TL alternator consists of several crucial components, each serving a specific purpose:
- Stator: The stator is a stationary part of the alternator that contains wire windings. These windings create a magnetic field when an electrical current flows through them.
- Rotor: The rotor is a rotating part of the alternator that is driven by the engine’s crankshaft. It consists of wire windings that produce a magnetic field when an electrical current passes through them.
- Rectifier: The rectifier is responsible for converting the alternating current (AC) produced by the alternator into direct current (DC) that can be used to charge the battery and power the vehicle’s electrical components.
- Voltage Regulator: The voltage regulator controls the output voltage of the alternator, ensuring it stays within a safe range. It prevents overcharging or undercharging of the battery and protects the electrical system from voltage spikes.
- Bearings: The alternator is supported by bearings that allow it to rotate smoothly. These bearings should be lubricated regularly to prevent friction and wear.
How Does the Alternator Charge the Battery?
When the engine is running, the alternator generates electricity and supplies it to the battery. As the alternator spins, the rotor creates a magnetic field that induces a current in the stator windings.
See Also: P0441 Acura Tlx: Definition Of P0441 Code And Its Causes
The current produced in the stator windings is then rectified by the rectifier, converting it into DC. This DC current flows to the battery, replenishing its charge and powering the vehicle’s electrical components.
Signs of a Failing Alternator

Recognizing the signs of a failing alternator is crucial to prevent unexpected breakdowns and electrical system failures. Here are some common indicators that your 2006 Acura TL alternator may be failing:
Dimming Headlights
If you notice that your headlights are dimming, especially when you accelerate or use other electrical components, it could be a sign of a failing alternator. A decrease in electrical power output from the alternator can cause the headlights to flicker or appear less bright than usual.
Dead Battery
A dead or constantly draining battery is another common sign of alternator issues. If your battery is relatively new and still loses charge frequently, it might be due to a malfunctioning alternator that is not properly charging the battery while the engine is running.
Unusual Noises
Strange noises coming from the alternator, such as grinding, squealing, or whining sounds, can indicate internal component failure. This could be due to worn-out bearings, a faulty voltage regulator, or other mechanical issues that require immediate attention.
Intermittent Electrical Failures
If you experience intermittent failures or malfunctions of electrical components, such as the radio, power windows, or dashboard lights, it could be a result of an inconsistent power supply from the alternator. These intermittent electrical failures are often a sign of impending alternator failure.
Burning Smell
A burning smell, especially when combined with other signs listed above, can indicate that the alternator is overheating.
This could be caused by a faulty voltage regulator or excessive electrical resistance within the alternator. Immediate action should be taken to prevent further damage or potential fire hazards.
Diagnosing Alternator Issues

Diagnosing potential alternator problems in your 2006 Acura TL requires a systematic approach. Here are some steps you can take to identify and troubleshoot alternator issues:
Step 1: Visual Inspection
Begin by visually inspecting the alternator and surrounding components for any obvious signs of damage, loose connections, or wear.
Look for frayed wires, loose belts, or signs of corrosion on the battery terminals. Ensure that all connections are secure and free from debris.
Step 2: Check Battery Voltage
Using a multimeter, measure the voltage across the battery terminals with the engine off. A healthy, fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts. If the voltage is significantly lower, it could indicate a problem with the alternator or battery.
See Also: P0441 Acura Mdx: Common Symptoms Of P0441 Code
Step 3: Start the Engine and Measure Voltage
Start the engine and measure the voltage across the battery terminals again. With the engine running, the voltage should read between 13.8 and 14.4 volts. If the voltage remains low or fluctuates excessively, it suggests a potential alternator issue.
Step 4: Load Test
You can also perform a load test to assess the alternator’s ability to handle electrical demands. With the engine running and all electrical components turned on, measure the voltage across the battery terminals. If the voltage drops significantly, it indicates an inadequate charging system.
Step 5: Seek Professional Help
If you are unsure about diagnosing or troubleshooting alternator issues, it is advisable to seek professional assistance.
Automotive technicians have the expertise and diagnostic tools to accurately identify and resolve alternator problems.
Step-by-Step Alternator Replacement Guide
Replacing the alternator in your 2006 Acura TL may seem daunting, but with the right tools and instructions, it can be done successfully. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
Step 1: Disconnect the Battery
Before starting any work on the alternator, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shocks and damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
Step 2: Locate the Alternator
The alternator is typically located near the front of the engine, mounted on brackets. Consult your vehicle’s manual or online resources to pinpoint the exact location of the alternator in your 2006 Acura TL.
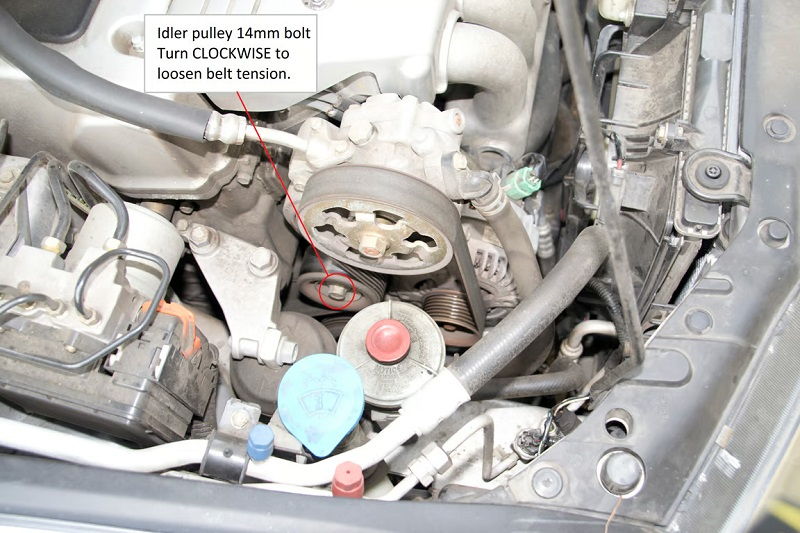
Step 3: Release Tension on the Serpentine Belt
Using a wrench or a tensioner tool, release tension on the serpentine belt by rotating the tensioner pulley. This will allow you to remove the belt from the alternator pulley.
Step 4: Disconnect Electrical Connections
Disconnect all electrical connections attached to the alternator, including the main power wire, voltage regulator plug, and any other connectors. Take note of their positions or take pictures to ensure proper reconnection later.
Step 5: Remove Mounting Bolts
Remove the mounting bolts that secure the alternator to the brackets. Depending on your vehicle, you may need to remove additional components or brackets to gain access to the alternator.
Step 6: Install the New Alternator
Position the new alternator in place and secure it with the mounting bolts. Reconnect all electrical connections to the new alternator, ensuring proper alignment and tightness.
Step 7: Reinstall the Serpentine Belt
Using the tensioner tool, release tension on the serpentine belt again and slide it back onto the alternator pulley. Make sure the belt is properly aligned with all other pulleys before releasing tension.
Step 8: Reconnect the Battery
Once you have completed the alternator replacement, reconnect the negative terminal of the battery to restore power to the vehicle’s electrical system.
Tips for Maintaining the Acura TL Alternator
Maintaining the alternator in your 2006 Acura TL is essential to ensure its longevity and optimal performance. Here are some tips to keep your alternator in top shape:
Regular Inspections
Periodically inspect the alternator and its surrounding components for any signs of wear, damage, or loose connections.
Check for frayed wires, loose belts, or signs of corrosionon the battery terminals. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage to the alternator and electrical system.
Cleanliness is Key
Keep the alternator and its surrounding area clean from dirt, debris, and oil buildup. Use a soft brush or cloth to gently remove any accumulated grime, ensuring that the vents and cooling fins are clear for proper airflow. This prevents overheating and extends the life of the alternator.
Keep Belts in Check
Regularly inspect the serpentine belt that drives the alternator for signs of wear, cracks, or fraying. Replace the belt if necessary to avoid slippage, which can lead to inadequate charging and potential alternator damage.
Maintain Proper Battery Health
A healthy battery is crucial for the alternator to function optimally. Regularly check the battery’s fluid levels, terminals, and connections to ensure they are clean and free from corrosion.
If the battery is showing signs of weakness or age, consider replacing it to avoid unnecessary strain on the alternator.
Monitor Electrical Load
Be mindful of the electrical load you put on your vehicle’s alternator. Running excessive accessories, such as high-powered audio systems or aftermarket lighting, can strain the alternator’s capabilities. Consider upgrading the alternator if you plan to add significant electrical load to your vehicle.
Drive Regularly
Extended periods of inactivity can lead to battery drain and alternator issues. If you don’t drive your vehicle regularly, consider using a battery maintainer or trickle charger to keep the battery charged and prevent strain on the alternator when starting the engine.
Upgrading the Alternator for Enhanced Performance
If you are looking to improve the electrical performance of your 2006 Acura TL or plan to add aftermarket accessories, upgrading the alternator may be a wise choice. Here are some factors to consider when upgrading:
Higher Amp Alternators
Higher amp alternators are designed to handle increased electrical loads and provide more power to your vehicle’s electrical system.
Consider upgrading to a higher amp alternator if you have added accessories like high-powered audio systems, aftermarket lighting, or other power-hungry components.
Compatibility Check
When upgrading the alternator, ensure compatibility with your vehicle’s electrical system and existing components.
Consult with a professional or refer to manufacturer guidelines to determine the correct alternator specifications for your specific model and needs.
Professional Installation
Upgrading the alternator may require modifications to your vehicle’s electrical system or mounting brackets.
It is recommended to have a professional install the upgraded alternator to ensure proper fitment, wiring, and overall functionality.
Warranty Considerations
When purchasing an upgraded alternator, check for warranty coverage. Some aftermarket alternators may offer extended warranties, providing peace of mind in case of any unforeseen issues or defects.
Common Alternator Issues and Troubleshooting
While the alternator in the 2006 Acura TL is a reliable component, it can still experience issues over time. Here are some common alternator problems and troubleshooting techniques:
Voltage Irregularities
If you notice erratic voltage readings or constant fluctuations on your vehicle’s voltage gauge, it could indicate a faulty voltage regulator or diode inside the alternator.
A failing voltage regulator may cause the alternator to produce excessive or insufficient voltage, leading to electrical system malfunctions.
Faulty Connections
Loose, corroded, or damaged electrical connections can disrupt the flow of electricity between the alternator and the battery.
Check all connections, including terminals, cables, and grounds, ensuring they are clean, tight, and free from corrosion. Clean and tighten connections as necessary to restore proper electrical flow.
Worn-out Bearings
Over time, the bearings that support the alternator’s rotor and pulley may wear out, leading to excessive noise, vibration, or even failure.
If you hear grinding or squealing noises from the alternator, it may indicate the need for bearing replacement. Consult a professional for proper diagnosis and replacement.
Testing Alternator Output
If you suspect an issue with your alternator, you can perform a simple output test using a multimeter. With the engine running, connect the multimeter to the battery terminals and measure the voltage output.
A healthy alternator should provide a voltage between 13.8 and 14.4 volts. If the reading is significantly lower, it may indicate an alternator problem.
Safety Precautions when Working with the Alternator
Working with the alternator in your 2006 Acura TL requires caution and adherence to safety procedures. Follow these safety precautions to protect yourself and prevent damage to your vehicle:
Disconnect the Battery
Before working on the alternator or any electrical components, always disconnect the negative terminal of the battery. This prevents the risk of electrical shock or accidental short circuits.
Use Proper Tools
Utilize the appropriate tools for the job to prevent damage to the alternator or surrounding components. For example, use a tensioner tool to relieve tension on the serpentine belt instead of using improper tools that may slip or cause injury.
Avoid Contact with Moving Parts
Take caution to avoid contact with any moving parts, such as the alternator pulley or engine belts, when working in the vicinity of the alternator. Ensure the engine is turned off and belts have stopped rotating before proceeding with any work.
Protective Gear
Wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, to protect yourself from any potential hazards or injury while working on the alternator.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines
Always refer to the vehicle manufacturer’s guidelines and instructions when working on the alternator. This ensures that you are following proper procedures specific to your vehicle, preventing any damage or safety hazards.
Exploring OEM and Aftermarket Alternator Options
When replacing the alternator in your 2006 Acura TL, you have the option to choose between original equipment manufacturer (OEM) or aftermarket alternators. Consider the following factors when deciding:
OEM Alternators
OEM alternators are manufactured by the same company that produced the original alternator in your vehicle. They are designed to meet the specifications and standards set by the manufacturer, ensuring proper fitment and performance.
Aftermarket Alternators
Aftermarket alternators are manufactured by third-party companies and may offer additional features or higher output capabilities compared to OEM alternators. They are often available at a lower cost and may provide more options for customization or performance enhancements.
Quality and Compatibility
Whether opting for OEM or aftermarket alternators, ensure that the chosen alternator is of high quality and compatible with your vehicle’s electrical system.
Research reviews, consult experts, or seek recommendations to ensure you select a reliable alternator that meets your specific needs.
Cost Considerations and Professional Alternator Services
The cost of alternator replacement in a 2006 Acura TL can vary depending on several factors, including the type of alternator, labor costs, and any additional components required.
However, it is essential to consider the long-term benefits and potential savings associated with professional alternator services:
Professional Expertise
Seeking professional alternator services ensures that the replacement or repair is carried out by experienced technicians with the necessary knowledge and tools. This reduces the risk of mistakes or further damage to the alternator or other components.
Warranty Coverage
Professional alternator services often come with warranty coverage, providing peace of mind in case of any issues or defects with the newly installed alternator. Warranty coverage can save you from additional expenses in the event of unexpected problems.
Long-Term Savings
While the cost of professional alternator services may be higher initially, it can save you money in the long run.
Proper installation, diagnosis, and maintenance by professionals can help prevent further damage to the alternator and electrical system, potentially avoiding costly repairs or replacements down the line.
Bringing this comprehensive guide to a close, we hope that the information provided here has shed light on the 2006 Acura TL alternator.
By understanding its functions, diagnosing potential issues, and following proper maintenance practices, Acura TL owners can ensure optimal electrical performance for their vehicles.
- P008C Fuel Cooler Pump Control Circuit Open - November 4, 2024
- P008D Fuel Cooler Pump Control Circuit Low - October 30, 2024
- P008E Fuel Cooler Pump Control Circuit High - October 26, 2024

