This post contains affiliate links. This means I will make a commission at no extra cost to you should you click through and make a purchase [ “As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.” ]. Read the full disclosure here.
Car Won’t Accelerate But RPMs Go Up GuideMechanic.Com Having a car that won’t accelerate even though the RPMs (revolutions per minute) are increasing can be frustrating and worrisome.
Understanding the possible causes behind this issue and finding the appropriate solutions is crucial to getting your vehicle back on the road safely.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various reasons why your car may experience this problem and explore the steps you can take to address it.
Before we delve into the possible causes, it’s important to note that a car’s engine works by converting fuel into energy, which ultimately propels the vehicle forward.
When the RPMs go up but the car doesn’t accelerate as expected, it indicates a problem with power delivery. This could be due to several factors, ranging from issues with the transmission, fuel system, or engine components. Let’s now explore some common causes for this frustrating phenomenon:
Car Won’t Accelerate But RPMs Go Up [ Transmission Issues ]
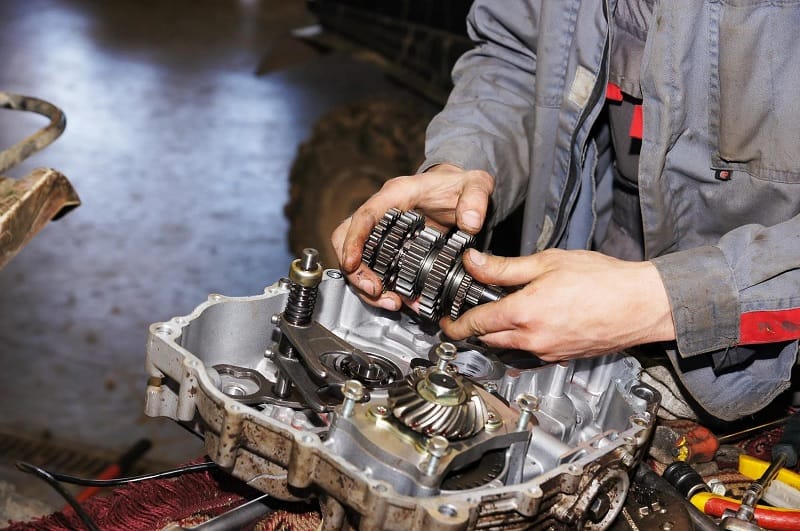

A malfunctioning transmission can often be the root cause behind a car’s failure to accelerate while the RPMs increase. Within the transmission system, there are several components that can contribute to this problem.
One possible culprit is a worn-out clutch. The clutch allows the engine’s power to transfer to the transmission and eventually to the wheels.
If the clutch is worn out, it may not engage properly, causing the car to struggle with acceleration despite the increased RPMs.
Another potential transmission issue is slipping transmission bands. These bands are responsible for holding gears in place.
If they become worn or damaged, they may slip and fail to engage the appropriate gear, resulting in a lack of acceleration.
Additionally, a faulty torque converter can also hinder acceleration. The torque converter is responsible for transferring power from the engine to the transmission. If it malfunctions, it may not deliver sufficient power to the wheels, causing the car to struggle with acceleration.
Identifying Transmission Issues
If you suspect a transmission issue, there are a few signs to look out for. One common indication is a delay in gear engagement.
When you shift gears, the car should respond quickly and smoothly. If there is a noticeable delay or if the gears grind when shifting, it may suggest a problem with the transmission.
Additionally, if you notice a burning smell or see transmission fluid leaks under your car, it’s crucial to have the transmission inspected as soon as possible.
Solutions for Transmission Issues
If you suspect a worn-out clutch, it will likely require replacement. This is a complex job that is best left to a qualified mechanic.
They will need to remove the transmission to access the clutch and replace it with a new one. Slipping transmission bands can also be resolved by a professional.
Depending on the severity of the issue, the transmission may need to be taken apart to replace or repair the bands. Similarly, a faulty torque converter will require professional attention. In some cases, it may be possible to repair the torque converter, but replacement is often necessary.
See Also : P0441 Evap Emission Control System
Regular maintenance and fluid checks can help prevent transmission issues. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and have the transmission fluid checked and replaced as needed. This will help ensure that the transmission operates smoothly and extends its lifespan.
Car Won’t Accelerate But RPMs Go Up [ Fuel System Problems ]
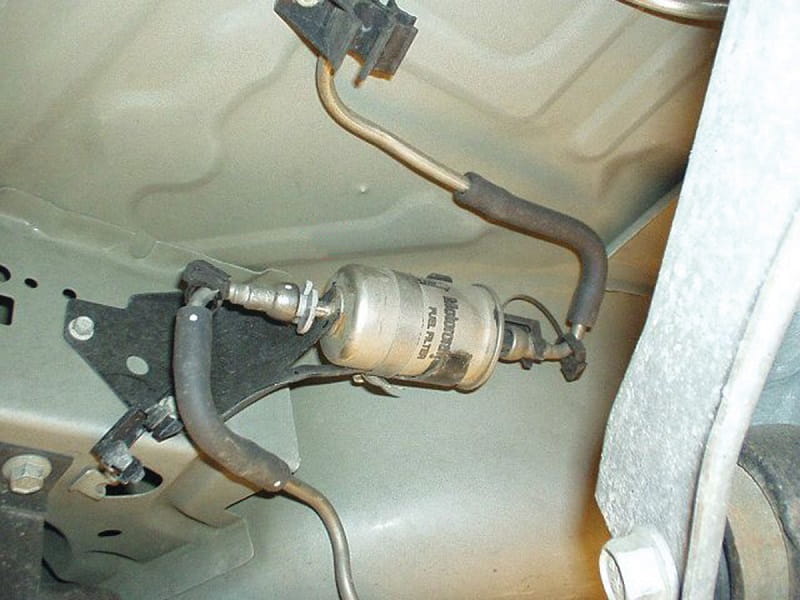

A well-functioning fuel system is essential for optimal engine performance and acceleration. Several components within the fuel system can affect power delivery.
One potential problem is a clogged fuel filter. The fuel filter is responsible for removing impurities and debris from the fuel before it reaches the engine.
If the filter becomes clogged, it can restrict the flow of fuel, resulting in poor acceleration despite the increased RPMs.
Another possible issue is a malfunctioning fuel pump. The fuel pump is responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine.
If it fails or becomes weak, it may not provide an adequate amount of fuel to the engine, causing a lack of power and acceleration.
Additionally, problems with the fuel injectors can also impact acceleration. The fuel injectors are responsible for injecting the precise amount of fuel into the combustion chamber. If they become clogged or develop leaks, it can disrupt the fuel delivery and affect acceleration.
Identifying Fuel System Problems
There are a few signs that may indicate fuel system issues. One common symptom is a sputtering engine. If the engine sputters or hesitates during acceleration, it may suggest a problem with the fuel system.
Additionally, if you notice a decrease in fuel efficiency or if the car struggles to start, it’s worth considering the fuel system as a potential culprit.
Unusual noises, such as whining or buzzing sounds coming from the fuel tank area, can also indicate fuel pump problems.
Solutions for Fuel System Problems
If you suspect a clogged fuel filter, it will need to be replaced. The fuel filter is typically located along the fuel line, either under the car or in the engine compartment.
It’s important to consult your car’s manual or a professional mechanic for the exact location and replacement procedure.
Similarly, a malfunctioning fuel pump will require replacement. The fuel pump is usually located inside the fuel tank, so accessing it can be a complex task. It’s generally recommended to have a professional handle this job to ensure it is done correctly.
Problems with fuel injectors can sometimes be resolved by using fuel injector cleaning additives. These additives can help remove deposits and improve fuel flow.
However, if the injectors are severely clogged or damaged, they may need to be replaced. It’s best to consult with a professional to determine the best course of action for your specific situation.
Car Won’t Accelerate But RPMs Go Up [ Engine Misfire]
An engine misfire occurs when one or more cylinders fail to ignite properly, resulting in a lack of power and decreased acceleration. Several factors can contribute to engine misfires.
One common cause is faulty spark plugs. Spark plugs are responsible for igniting the fuel mixture in the combustion chamber.
If they become worn or fouled, they may not create a strong spark, leading to misfires. Another possible cause is a malfunctioning ignition coil.
The ignition coil generates the high voltage needed to ignite the spark plugs. If it fails, it can result in misfires and poor acceleration.
Additionally, the oxygen sensor plays a crucial role in engine performance. It measures the oxygen content in the exhaust gases and helps the engine adjust the air-fuel mixture accordingly. A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can provide incorrect readings, leading to misfires and a lack of acceleration.
Identifying Engine Misfires
There are several signs that may indicate engine misfires. One common symptom is a rough idle. If the engine feels shaky or unstable when idling, it may suggest misfires.
Additionally, if you notice a loss of power during acceleration or if the car hesitates and jerks while driving, it’s worth considering engine misfires as a possible cause. The check engine light may also illuminate, indicating a problem with the engine.
Solutions for Engine Misfires
If you suspect faulty spark plugs, they will need to be replaced. It’s important to use the appropriate spark plugs recommended by the manufacturer for your specific car model.
The ignition coil can also be a potential culprit, and if it is found to be faulty, it should be replaced. It’s recommended to replace all spark plugs and ignition coils at once to ensure optimal performance and prevent future issues.
If the oxygen sensor is the cause of the misfires, it will need to be replaced. The oxygen sensor is typically located in the exhaust system, either before or after the catalytic converter. It’s important to consult your car’s manual or a professional mechanic to locate and replace the sensor properly.
Car Won’t Accelerate But RPMs Go Up [ Throttle Body Malfunction ]
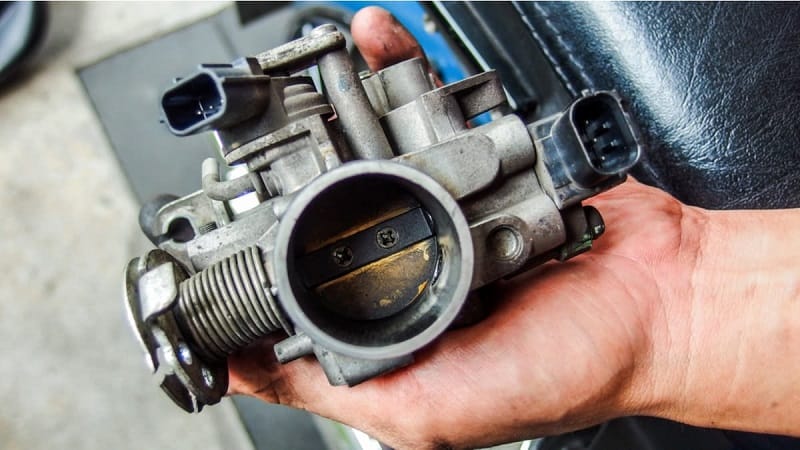

The throttle body is responsible for controlling the amount of air that enters the engine. If it becomes dirty or malfunctions, it may not open properly, leading to reduced acceleration.
Over time, carbon deposits can accumulate on the throttle body, affecting its operation. Additionally, the throttle position sensor, which communicates the position of the throttle to the engine control unit, can also malfunction, leading to poor acceleration.
Identifying Throttle Body Malfunctions
If the throttle body is the source of the problem, there are a few signs to watch out for. One common indication is a lack of responsiveness when pressing the accelerator pedal.
If you notice a delay or sluggishness in throttle response, it may suggest a problem with the throttle body. Additionally, if the car’s idle speed is irregular or fluctuates, it’s worth considering the throttle body as a potential culprit.
Solutions for Throttle Body Malfunctions
Regular maintenance can help prevent throttle body malfunctions. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals and have the throttle body cleaned at the appropriate intervals.
Cleaning the throttle body involves removing it from the engine and using a specialized cleaner to remove any carbon deposits or debris. It’s best to consult your car’s manual or a professional mechanic for the specific cleaning procedure.
If the throttle position sensor is the cause of the problem, it will need to be replaced. The throttle position sensor is typically located on the throttle body itself.
It’s important to consult your car’s manual or a professional mechanic for the exact location and replacement procedure.
Car Won’t Accelerate But RPMs Go Up [ Ignition System Problems ]

The ignition system plays a crucial role in the combustion process and engine performance. Several components within the ignition system can contribute to poor acceleration. One potential problem is a malfunctioning ignition coil.
The ignition coil generates the high voltage needed to ignitethe spark plugs. If the ignition coil fails, it can result in weak or inconsistent sparks, leading to poor acceleration.
Another possible issue is a faulty distributor cap. The distributor cap distributes the high voltage from the ignition coil to the individual spark plugs. If it becomes worn or damaged, it can disrupt the spark distribution, causing misfires and a lack of power.
Additionally, spark plug wires that are worn or damaged can also affect ignition performance. These wires carry the high voltage from the ignition coil to the spark plugs.
If they are in poor condition, they may not deliver the necessary voltage, resulting in weak sparks and decreased acceleration.
Identifying Ignition System Problems
There are a few signs that may indicate ignition system problems. If you notice a rough idle, a decrease in fuel efficiency, or a loss of power during acceleration, it’s worth considering the ignition system as a potential cause. Additionally, if you experience difficulty starting the car or if the engine misfires, it may suggest ignition system issues.
Solutions for Ignition System Problems
If you suspect a faulty ignition coil, it will need to be replaced. The ignition coil is usually located near the engine, and it’s important to consult your car’s manual or a professional mechanic for the exact location and replacement procedure.
Similarly, a worn or damaged distributor cap will require replacement. The distributor cap is typically located on top of the engine, and it’s crucial to replace it with a high-quality cap that is compatible with your car’s make and model.
If the spark plug wires are the cause of the problem, they should be replaced. It’s important to use high-quality wires that are specifically designed for your car’s ignition system. When replacing the wires, it’s advisable to replace them one at a time to ensure that the correct connection is maintained.
Regular maintenance of the ignition system is essential to prevent problems. This includes periodic inspection and replacement of spark plugs, ignition coils, distributor caps, and spark plug wires according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Keeping the ignition system in good working condition will help ensure optimal engine performance and acceleration.
Car Won’t Accelerate But RPMs Go Up [ Exhaust System Blockage ]

A blocked or restricted exhaust system can have a significant impact on engine performance and acceleration. The exhaust system is responsible for expelling exhaust gases from the engine.
If it becomes blocked or restricted, it can prevent the engine from effectively expelling gases, resulting in reduced power and acceleration.
One common cause of exhaust system blockage is a clogged catalytic converter. The catalytic converter is designed to reduce harmful emissions by converting them into less harmful substances.
Over time, it can become clogged with carbon deposits or other debris, restricting the flow of exhaust gases. Another potential issue is a damaged muffler.
The muffler is responsible for reducing noise produced by the exhaust gases. If it becomes damaged or corroded, it can impede the flow of gases, affecting engine performance.
Identifying Exhaust System Blockage
There are a few signs that may indicate exhaust system blockage. If you notice a decrease in engine power, poor acceleration, or a decrease in fuel efficiency, it’s worth considering a blocked exhaust system as a potential cause.
Additionally, if you hear a loud hissing or popping noise coming from the exhaust system or notice a strong smell of exhaust fumes, it may suggest a problem with the catalytic converter or muffler.
Solutions for Exhaust System Blockage
If a clogged catalytic converter is the cause of the problem, it will likely need to be replaced. The catalytic converter is usually located in the exhaust system, between the engine and the muffler.
It’s important to consult your car’s manual or a professional mechanic for the specific location and replacement procedure.
In some cases, it may be possible to clean the catalytic converter using specialized cleaning solutions, but replacement is often the most effective solution.
If a damaged muffler is the culprit, it will also need to be replaced. The muffler is typically located at the rear of the exhaust system, and it’s important to choose a replacement muffler that is compatible with your car’s make and model.
Replacing the muffler may also involve replacing other components of the exhaust system, such as pipes or hangers, depending on the extent of the damage.
Car Won’t Accelerate But RPMs Go Up [ Faulty Sensors ]

Modern cars rely on various sensors to monitor and regulate engine performance. If these sensors malfunction, they can have a significant impact on acceleration.
Several sensors can contribute to poor acceleration, including the throttle position sensor, mass airflow sensor, and engine control unit (ECU).
The throttle position sensor measures the position of the throttle and communicates this information to the engine control unit.
If the sensor malfunctions or provides inaccurate readings, it can affect the fuel-air mixture and throttle response, resulting in poor acceleration.
The mass airflow sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine and helps determine the appropriate fuel injection. If it fails or becomes dirty, it can disrupt the air-fuel ratio and impact acceleration.
The engine control unit is responsible for controlling various engine functions based on the information received from sensors.
If the ECU malfunctions, it can affect fuel delivery, ignition timing, and other parameters, leading to decreased acceleration.
Identifying Faulty Sensors
Diagnosing faulty sensors can be challenging without specialized diagnostic equipment. However, there are some common signs that may indicate sensor problems.
If you notice a lack of responsiveness when pressing the accelerator pedal, irregular engine idling, or a decrease in fuel efficiency, it may suggest sensor malfunctions.
Additionally, if the check engine light illuminates and the onboard diagnostic system indicates sensor-related error codes, it’s worth considering sensor issues as a potential cause.
Solutions for Faulty Sensors
Diagnosing and replacing faulty sensors can be complex and typically requires professional expertise. A qualified mechanic will use diagnostic equipment to identify specific sensor malfunctions.
Once the problematic sensor is identified, it can be replaced following the manufacturer’s recommendations. It’s important to use high-quality sensors that are compatible with your car’s make and model to ensure proper functionality.
Car Won’t Accelerate But RPMs Go Up [ Limited Air Supply ]

Inadequate air supply to the engine can also affect acceleration. The engine requires a sufficient amount of air for proper combustion and power generation. Several factors can contribute to limited air supply, including a dirty or clogged air filter.
The air filter is responsible for removing dust, dirt, and other particles from the incoming air before it enters the engine.
Over time, the filter can become clogged with debris, restricting airflow and affecting engine performance. If the engine doesn’t receive enough air, it may struggle to produce power, resulting in poor acceleration.
Identifying Limited Air Supply
A few signs may indicate limited air supply to the engine. If you notice a decrease in engine power, poor acceleration, or a decrease in fuel efficiency, it’s worth considering a clogged air filter as a potential cause.
Additionally, if the engine runs rough or if you hear unusual noises coming from the air intake area, it may suggest a problem with the air filter.
Solutions for Limited Air Supply
If you suspect a clogged air filter, it will need to be replaced. The air filter is usually located in a housing near the engine or in the air intake duct.
It’s important to consult your car’s manual or a professional mechanic for the specific location and replacement procedure.
Regularly inspecting and replacing the air filter according to the manufacturer’s recommendations will help ensure optimal airflow to the engine and maintain acceleration performance.
Car Won’t Accelerate But RPMs Go Up [ Traction Control or Stability Control Intervention ]

Some modern cars are equipped with traction control or stability control systems that can limit power delivery in certain situations.
These systems are designed to improve safety by preventing wheel slippage and maintaining vehicle stability. When these systems detect wheel slippage or loss of control, they may intervene and reduce engine power, giving the impression of poor acceleration.
Identifying Traction Control or Stability Control Intervention
If your car is equipped with traction control or stability control systems, you may notice a decrease in engine power during certain driving conditions.
If the engine power is reduced when accelerating on slippery surfaces or during aggressive maneuvers, it may suggest intervention from these systems.
Additionally, the dashboard may display warning lights or messages indicating traction control or stability control activation.
Solutions for Traction Control or Stability Control Intervention
If you experience reduced engine power due to traction control or stability control intervention, it’s important to understand that these systems are designed to enhance safety.
In most cases, there is no action required on your part, as the systems will automatically adjust engine power to maintain control and stability.
However, if you believe the intervention is occurring unnecessarily or excessively, it’s advisable to have the system inspected by a professional to ensure it is functioning correctly.
Car Won’t Accelerate But RPMs Go Up [ Electrical Issues ]

Faulty electrical connections, damaged wiring, or a weak battery can all contribute to acceleration problems. The electrical system in a car is responsible for powering various components, including ignition systems, fuel systems, and sensors.
If there is an issue with the electrical system, it can disrupt the proper functioning of these components and affect acceleration.
Identifying Electrical Issues
Diagnosing electrical issues can be challenging without specialized equipment. However, there are some signs that may indicate electrical problems.
If you notice intermittent engine power loss, flickering lights, or if the car struggles to start, it may suggest electrical issues.
Additionally, if the battery warning light illuminates on the dashboard, it’s worth considering electrical system problems as a potential cause.
Solutions for Electrical Issues
Diagnosing and resolving electrical issues typically requires professional expertise. A qualified mechanic will use diagnostic equipment to identify the specific electrical problem.
Depending on the issue, it may involve repairing or replacing damaged wiring, connectors, or componentswithin the electrical system.
If the battery is weak or failing, it will need to be replaced. It’s important to use a high-quality battery that is compatible with your car’s specifications.
Regular maintenance of the electrical system is essential to prevent issues. This includes checking and tightening electrical connections, inspecting wiring for any signs of damage or wear, and ensuring the battery is in good working condition.
Additionally, following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and addressing any electrical issues promptly will help maintain optimal acceleration performance.
In conclusion, a car that won’t accelerate despite the increasing RPMs can be attributed to various factors. Transmission issues such as a worn-out clutch, slipping transmission bands, or a faulty torque converter can hinder power delivery.
Fuel system problems like a clogged fuel filter, malfunctioning fuel pump, or issues with fuel injectors can restrict fuel flow and impact acceleration.
Engine misfires caused by faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or oxygen sensors can result in a lack of power. Malfunctions in the throttle body, ignition system, exhaust system, sensors, limited air supply, or electrical system can also contribute to poor acceleration.
Identifying the specific cause behind the acceleration problem requires careful diagnosis and professional expertise. It’s crucial to consult a qualified mechanic who can accurately identify the issue and recommend the appropriate solutions.
Regular maintenance, including checking and replacing faulty components, following manufacturer’s recommendations, and addressing any issues promptly, is key to preventing acceleration problems and ensuring optimal engine performance.
Remember, maintaining a well-functioning vehicle not only enhances your driving experience but also contributes to overall safety on the road.
If you encounter acceleration issues, don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance to address the problem and get your car back to its optimal performance.
- 4×4 Truck for Sale Under 20K - October 15, 2025
- 4×4 Truck for Sale QLD - October 12, 2025
- 4×4 Truck for Sale Under 10000 - October 9, 2025
