This post contains affiliate links. This means I will make a commission at no extra cost to you should you click through and make a purchase [ “As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.” ]. Read the full disclosure here.
Deciphering P0037: Understanding HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 1 Sensor 2) GuideMechanic.Com In the intricate language of automotive diagnostics, trouble codes serve as critical indicators of underlying issues within a vehicle’s systems.
One such code, P0037, shines a spotlight on the HO2S (Heated Oxygen Sensor) Heater Control Circuit being detected as low for Bank 1 Sensor 2.
In this comprehensive article, we embark on a journey to unravel the complexities surrounding P0037, exploring its significance, potential causes, diagnostic procedures, and effective solutions.
See Also: P0035 Turbo Charger Bypass Valve Control Circuit High
P0037 HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
Understanding P0037:
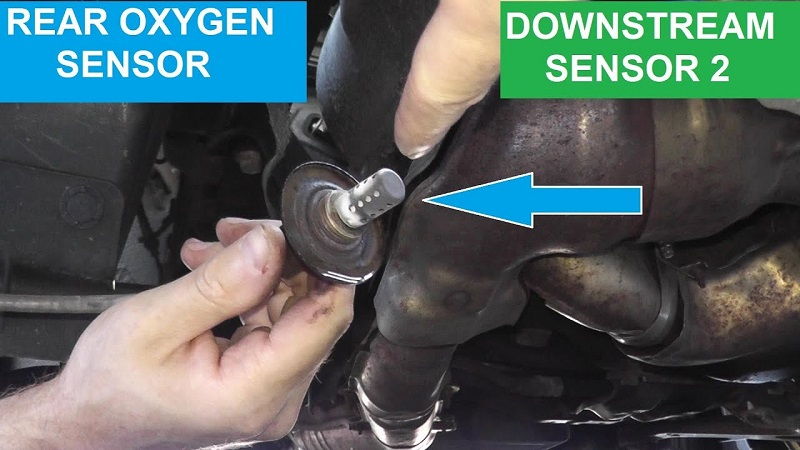
P0037 is part of the OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) system, a standardized protocol implemented in vehicles to monitor and report malfunctions related to engine performance and emissions control.
Specifically, P0037 signifies an anomaly in the HO2S Heater Control Circuit for Bank 1 Sensor 2. To grasp the implications of this code, it’s essential to understand the role of the heated oxygen sensor in the vehicle’s exhaust system.
The heated oxygen sensor, or HO2S, is a crucial component tasked with monitoring the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. This information is vital for the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the air-fuel mixture accurately, optimizing combustion efficiency and reducing emissions.
Bank 1 Sensor 2 refers to the specific sensor located downstream from the catalytic converter in bank 1 of the engine (typically the side with cylinder 1), which monitors oxygen levels after the exhaust gases have undergone treatment.
When the Heater Control Circuit for this sensor is detected as low (P0037), it indicates a potential issue with the electrical circuit responsible for heating the sensor element.
Proper sensor heating is crucial for accurate and timely feedback to the ECU, particularly during cold start conditions when exhaust gases are cooler and sensor responsiveness is essential for efficient engine operation.
P0037 HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
Common Causes of P0037:

Diagnosing the root cause of P0037 requires a systematic approach and a keen understanding of automotive electrical systems.
While precise diagnosis often necessitates specialized tools and expertise, several common culprits are typically associated with this trouble code:
Faulty HO2S Heater Element:
The heating element within the oxygen sensor may fail due to age, wear, or manufacturing defects, resulting in reduced or no heating capacity.
Wiring Issues:
Any abnormalities in the wiring harness connected to the HO2S Heater Control Circuit can lead to a low voltage condition, such as frayed wires, corroded connections, or short circuits.
Faulty Relay or Fuse:
A malfunctioning relay or fuse in the circuit responsible for supplying power to the HO2S heater can disrupt heating operation, resulting in the P0037 code.
ECU Malfunction:
In rare cases, the issue may lie with the engine control unit itself, which fails to send the appropriate signals to activate the HO2S heater circuit.
Environmental Factors:
Extreme temperatures or environmental conditions can affect the performance of the HO2S heater, potentially leading to P0037.
P0037 HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
Diagnostic Procedures:
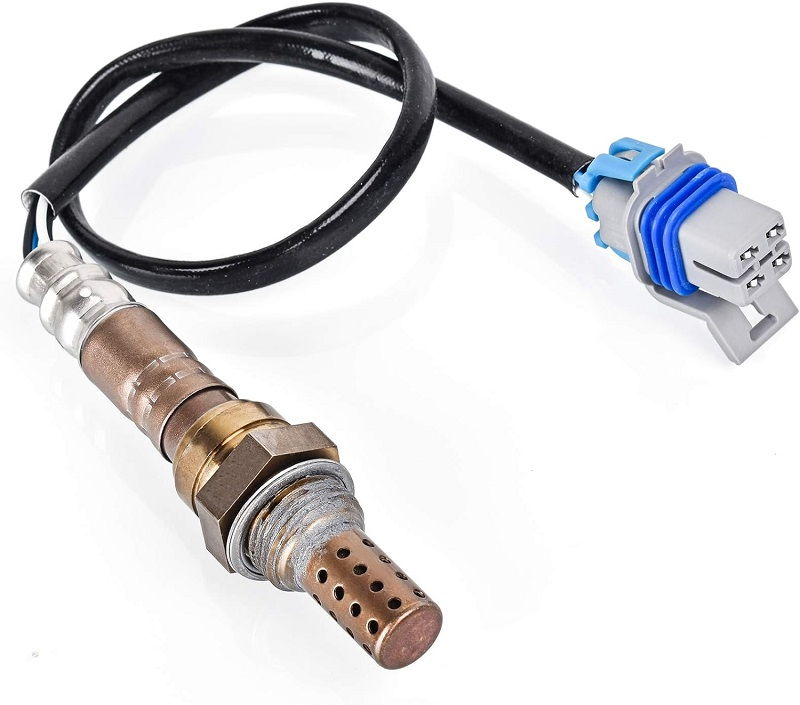

To diagnose and address P0037 effectively, automotive technicians typically follow these steps:
Code Retrieval:
Utilize an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the trouble code (P0037) stored in the vehicle’s ECU. This confirms the presence of the issue and provides a starting point for diagnosis.
Visual Inspection:
Conduct a thorough visual inspection of the wiring harness, connectors, and associated components related to the HO2S Heater Control Circuit. Look for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
Test Heater Circuit Voltage:
Using a multimeter or specialized diagnostic tool, measure the voltage at various points along the HO2S Heater Control Circuit to identify any abnormalities or voltage drops.
Inspect HO2S Heater Element:
Test the resistance of the HO2S heater element using an ohmmeter to determine if it is within the manufacturer’s specified range. A deviation from this range indicates a faulty sensor requiring replacement.
Check Relay and Fuse:
Inspect the relay and fuse associated with the HO2S Heater Control Circuit to ensure they are functioning correctly. Replace any defective components as necessary.
Verify ECU Signals:
Use a diagnostic tool to monitor the signals sent by the ECU to activate the HO2S heater circuit. Ensure that the ECU is providing the appropriate commands to initiate heating.
Potential Solutions:
Based on diagnostic findings, several solutions may be required to rectify P0037:
Replace HO2S:
If the heated oxygen sensor is found to be faulty, replace it with a new sensor to restore proper functionality.
Repair Wiring Issues:
Address any wiring problems identified during inspection, such as repairing damaged wires, replacing connectors, or improving grounding connections.
Replace Relay or Fuse:
If the relay or fuse is determined to be defective, replace it with a new one to ensure proper power supply to the HO2S heater circuit.
Rectify ECU Issues:
If the issue lies with the ECU, consult with a qualified technician to determine the appropriate course of action, which may involve repairing or replacing the ECU.
Address Environmental Factors:
Take measures to protect the HO2S heater from extreme temperatures or environmental conditions that may affect its performance.
Conclusion:
See Also: P0036 HO2S Heater Control Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
P0037, signaling a low voltage condition in the HO2S Heater Control Circuit for Bank 1 Sensor 2, underscores the importance of precise sensor operation in modern vehicle emissions control systems.
By following systematic diagnostic procedures and addressing potential causes such as faulty components or wiring issues, automotive technicians can effectively resolve P0037 and restore optimal engine performance and efficiency.
Regular maintenance and proactive troubleshooting are essential for identifying and addressing trouble codes promptly, ensuring vehicles operate smoothly and comply with emissions regulations.
- Catalytic Converter Cleaner Nearby - April 25, 2025
- BMW Catalytic Converter Price: What You Need to Know - April 24, 2025
- Scrap Catalytic Converter Price - April 24, 2025
