This post contains affiliate links. This means I will make a commission at no extra cost to you should you click through and make a purchase [ “As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.” ]. Read the full disclosure here.
Unveiling the Culprits: What Causes Low Transmission Line Pressure? GuideMechanic.Com Transmission line pressure is a critical aspect of any vehicle’s operation, ensuring smooth gear changes and optimal performance on the road.
However, when transmission line pressure drops below normal levels, it can lead to a range of issues that affect drivability and reliability.
Understanding the root causes of low transmission line pressure is essential for diagnosing and resolving these problems effectively.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the various factors that can contribute to low transmission line pressure and discuss the steps to address them.
See Also: 4l60e Transmission External Wiring Harness Diagram
What Causes Low Transmission Line Pressure?
Introduction

Transmission line pressure refers to the hydraulic pressure generated within the transmission system to engage and disengage gears during shifting.
This pressure is crucial for maintaining proper clutch engagement, preventing slippage, and ensuring smooth transitions between gears.
When the transmission line pressure falls below the recommended levels, it can result in symptoms such as harsh shifting, slipping gears, and reduced overall performance.
Common Causes of Low Transmission Line Pressure
Low Transmission Fluid Level:
One of the most common causes of low transmission line pressure is insufficient transmission fluid. Low fluid levels can restrict the flow of hydraulic fluid, leading to decreased pressure within the transmission system. This can occur due to leaks, improper maintenance, or normal wear and tear over time.
Worn or Damaged Transmission Components:
Check out this Power Steering Cooler

Wear and tear on internal transmission components, such as seals, gaskets, and valve bodies, can compromise the integrity of the system and contribute to low line pressure. Damaged or worn-out components may allow fluid to bypass or leak, reducing pressure levels and affecting performance.
Clogged or Restricted Transmission Fluid Passages:
Over time, transmission fluid can become contaminated with debris, dirt, and metal particles, leading to the accumulation of sludge and deposits within the transmission system. These deposits can clog or restrict fluid passages, impeding the flow of hydraulic fluid and causing a drop in line pressure.
Faulty Pressure Regulator Valve:
The pressure regulator valve is responsible for controlling and regulating the transmission line pressure. A malfunctioning or stuck pressure regulator valve can disrupt the pressure regulation process, leading to fluctuations or reductions in line pressure.
Faulty Transmission Pump:
The transmission pump is responsible for circulating transmission fluid throughout the system and generating hydraulic pressure. A faulty or worn-out transmission pump may fail to maintain adequate pressure levels, resulting in low line pressure and related symptoms.
Incorrect Transmission Fluid Type:
Using the wrong type or viscosity of transmission fluid can affect its ability to maintain proper pressure levels within the transmission system. It’s essential to use the manufacturer-recommended transmission fluid to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Cooling System Issues:
Transmission fluid is typically cooled by the vehicle’s cooling system to prevent overheating. If the cooling system is compromised due to issues such as a faulty radiator, thermostat, or cooling lines, it can lead to overheating of the transmission fluid and subsequent pressure drops.
See Also: 4l60e Rebuild Cost from $1500 to $2500
What Causes Low Transmission Line Pressure?
Diagnosing and Addressing
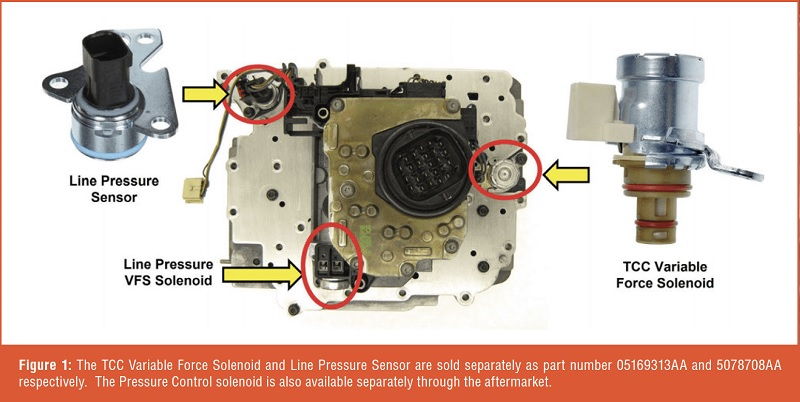
Diagnosing and addressing low transmission line pressure requires a systematic approach and thorough inspection of the transmission system. Here are the steps involved in diagnosing and resolving this issue:
Check Transmission Fluid Level and Condition:
Start by checking the transmission fluid level and condition using the dipstick or inspection port. If the fluid level is low or the fluid appears dark, dirty, or contaminated, it may indicate a potential issue with the transmission system.
Inspect for Leaks:
Inspect the transmission system, including the transmission pan, seals, gaskets, cooler lines, and hoses, for any signs of leaks or fluid seepage. Address any leaks promptly and replace damaged components as needed.
Perform a Pressure Test:
Use a transmission pressure gauge to measure the line pressure at various points within the transmission system. Compare the measured pressure readings to the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the pressure is within the acceptable range.
Inspect Transmission Components:
Inspect internal transmission components, such as the valve body, pressure regulator valve, transmission pump, and clutch packs, for signs of wear, damage, or malfunction. Replace any worn or damaged components and clean or flush the transmission system to remove any contaminants.
Flush and Replace Transmission Fluid:
If the transmission fluid is contaminated or degraded, perform a complete transmission fluid flush and replace it with fresh, manufacturer-recommended fluid. Flushing the transmission system helps remove any sludge, debris, or contaminants that may be contributing to low line pressure.
Check and Adjust Pressure Regulator Valve:

Inspect the pressure regulator valve for proper operation and adjust or replace it if necessary. Ensure that the valve is free from any debris or obstructions that may affect its performance.
Address Cooling System Issues:
Check the vehicle’s cooling system for any issues that may affect the transmission fluid temperature, such as a faulty radiator, thermostat, or cooling lines. Repair or replace any faulty components to ensure proper cooling of the transmission fluid.
Seek Professional Assistance:
If you’re unable to diagnose or resolve the issue on your own, seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or transmission specialist. They have the expertise and diagnostic equipment to identify and address complex transmission problems effectively.
What Causes Low Transmission Line Pressure?
Conclusion

Low transmission line pressure can have a significant impact on your vehicle’s performance, reliability, and safety. By understanding the common causes of this issue and following the appropriate diagnostic and repair procedures, you can effectively diagnose and resolve low transmission line pressure problems.
See Also: P0441-00 Range Rover
Remember to perform regular maintenance, including checking transmission fluid levels and condition, to prevent potential issues and ensure optimal transmission performance for years to come.
- Catalytic Converter Replacement Cost for Subaru Forester - April 28, 2025
- Ford F-150 Catalytic Converter Replacement Cost - April 28, 2025
- Ford Fiesta Catalytic Converter Replacement Cost - April 28, 2025
